partitioning¶
Within an installation section, the partitioning sub-section allows you to describe an advanced partitioning table.
Warning
not all clouds support advanced partitioning. When building a machine image for an environment that does not support advanced partitioning, the build will fail with an appropriate error message.
The definition of a partitioning section is:
"partitioning": {
...the partitioning definition goes here.
}
The valid keys to use within partitioning are:
disks(mandatory): an array of objects describing the physical disks that make up the advanced partitioning table. A disk may include up to four partitions, one of which can be of type extended that may hold one or more logical partitions. For more information, refer to the disks sub-section.volumeGroups(optional): an array objects describing any volume groups that make up the advanced partitioning table. If used, you must have one or more logical volumes using this volume group. For more information, refer to the volumeGroups sub-section.logicalVolumes(optional): an array of objects describing any logical volumes that make up the partitioning table. If used, you must have one or more volume groups that are used in creating the logical volume. For more information, refer to the logical volumes sub-section.
Examples¶
Basic Example¶
The following example describes a partitioning table with one disk that has three partitions: the boot partition, a swap partition and a third partition called space.

{
"partitioning": {
"disks": [
{
"name": "sda",
"type": "msdos",
"size": 12288,
"partitions": [
{
"number": 1,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 2048,
"mountPoint": "/boot"
},
{
"number": 2,
"fstype": "linux-swap",
"size": 1024
},
{
"number": 3,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 9216,
"label": "space",
"mountPoint": "/space"
}
]
}
]
}
}
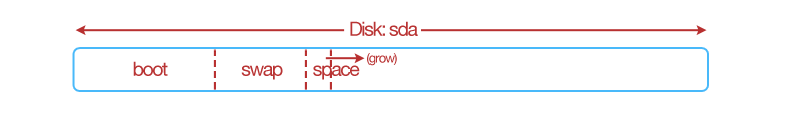
Using Growable Example¶
The same partitioning table as shown in Basic Example can be written slightly differently using the grow flag. A growable partition is partition that takes up the rest of the available disk space after the other partition sizes have been satisfied. In this case, we say that the “space” partition takes up the rest of the disk (rather than us having to calculate the space left after creating the first two partitions). We must specify though a size for the third partition (the minimum partition size is 64MB).
{
"partitioning": {
"disks": [
{
"name": "sda",
"type": "msdos",
"size": 12288,
"partitions": [
{
"number": 1,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 2048,
"mountPoint": "/boot"
},
{
"number": 2,
"fstype": "linux-swap",
"size": 1024
},
{
"number": 3,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 64,
"grow": true,
"label": "space",
"mountPoint": "/space"
}
]
}
]
}
}
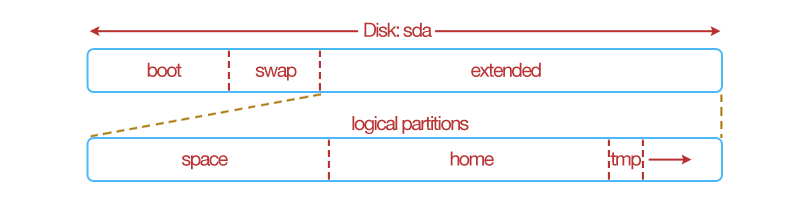
Creating Logical Partitions Example¶
In this example the, logical partitions are created inside the space partition. The space partition now has the filesystem type Extended.
..warning:: only one partition within a disk can have logical partitions. When a partition is extended, you cannot specify a mount point or a label. Logical partitions must start with number 5
{
"partitioning": {
"disks": [
{
"name": "sda",
"type": "msdos",
"size": 12288,
"partitions": [
{
"number": 1,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 2048,
"mountPoint": "/boot"
},
{
"number": 2,
"fstype": "linux-swap",
"size": 1024
},
{
"number": 3,
"fstype": "Extended",
"size": 9216,
"partitions": [
{
"number": 5,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 4098,
"mountPoint": "/space",
"label": "space"
},
{
"number": 6,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 4098,
"mountPoint": "/home",
"label": "home"
},
{
"number": 7,
"fstype": "ext3",
"size": 64,
"mountPoint": "/tmp",
"label": "tmp",
"grow": true
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
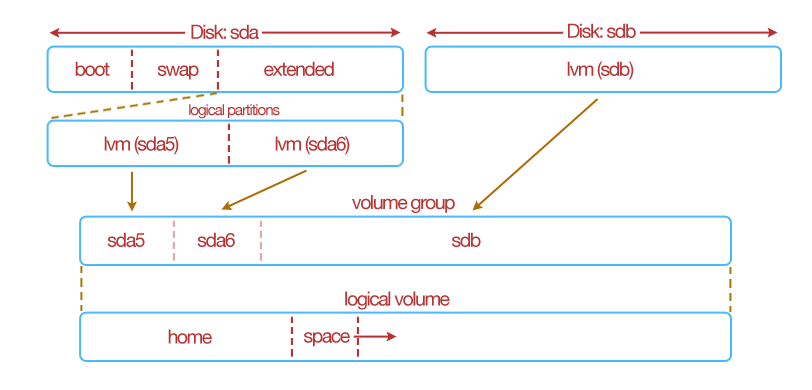
Volume Groups and Logical Volumes Example¶
The following example shows how disks and partitions that have lvm filesystem types can be regrouped together – volume group then re-partitioned differently – a logical volume.
{
"partitioning": {
"disks": [
{
"name": "sda",
"type": "msdos",
"size": 12288,
"partitions": [
{
"number": 1,
"fstype": "ext3",
"mountPoint": "/boot",
"size": 1024
},
{
"number": 2,
"fstype": "linux-swap",
"size": 1024
},
{
"number": 3,
"fstype": "extended",
"size": 64,
"grow": true,
"partitions": [
{
"number": 5,
"fstype": "lvm2",
"size": 5120
},
{
"number": 6,
"fstype": "lvm2",
"size": 5120
}
]
}
]
},
{
"name": "sdb",
"type": "lvm",
"size": 122880
}
],
"volumeGroups": [
{
"name": "grp1",
"physicalVolumes": [
{
"name": "sda5"
},
{
"name": "sda6"
},
{
"name": "sdb"
}
]
}
],
"logicalVolumes": [
{
"name": "vol1",
"vg_name": "grp1",
"fstype": "ext3",
"mountPoint": "/home",
"size": 4098
},
{
"name": "vol2",
"vg_name": "grp1",
"fstype": "ext3",
"mountPoint": "/space",
"size": 64,
"grow": true
}
]
}
}